Key Takeaways
- Apprenticeships help bridge the skills gap by giving students real-world training and career pathways.
- Diversity and inclusion initiatives expand the labor pool and foster stronger, more innovative teams.
- Technology improves efficiency, safety, and workflow management, reducing pressure from labor shortages.
- Partnerships with schools and training institutions strengthen talent pipelines and align education with industry needs.
- Government investments support upskilling, workforce development, and long-term industry resilience.
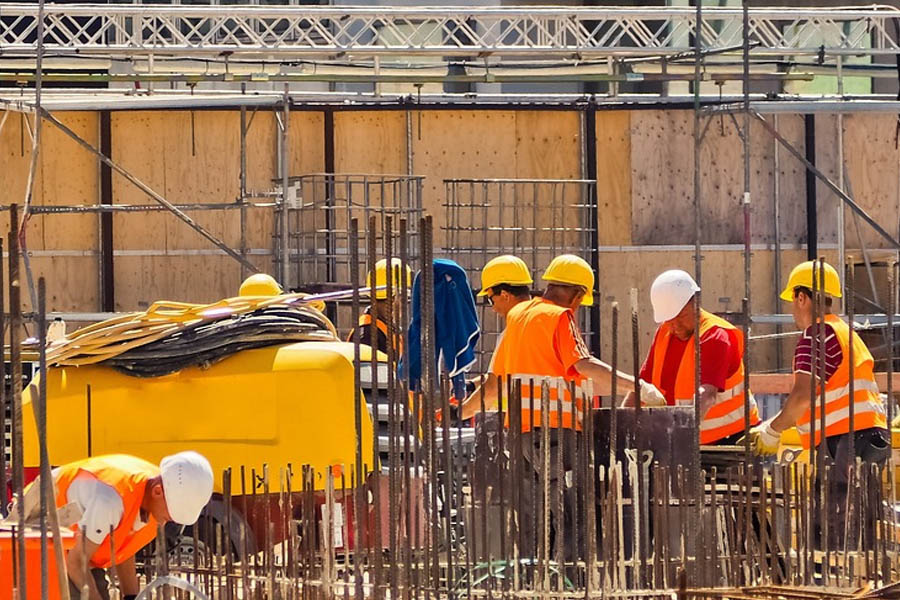
The construction industry continues to grapple with a persistent workforce shortage driven by an aging labor pool, rapid infrastructure growth, and evolving skill requirements. Companies across the sector face challenges in filling both entry-level and specialized roles, which can slow project timelines and increase operational costs. As the demand for modernized buildings, transportation systems, and energy facilities rises, the need for fresh talent becomes even more critical.
To remain resilient, many organizations are now exploring innovative strategies that strengthen recruitment, training, and long-term workforce development. These approaches include adopting new technologies, enhancing career pathways, and fostering collaboration among industry stakeholders. For readers interested in learning more about solutions that can support workforce improvement, click here to access additional insights. By embracing creative and forward-thinking methods, the construction industry can build a stronger talent pipeline capable of meeting the demands of future projects.
Apprenticeship Programs
Modern apprenticeship programs benefit both future workers and employers dealing with labor shortages. In Wisconsin, over 11,000 youth apprentices in the construction trades are enrolled for the 2024-2025 period, marking a 14% increase from the previous year. These initiatives exemplify a national trend in which schools partner with construction companies to connect classroom education with hands-on work. Apprenticeships offer high school students practical experience, helping to close the skills gap and enabling them to launch their careers before graduation. Students earn while they learn, with straightforward pathways to apprenticeships and construction employment that become more appealing as college expenses rise. Supported across party lines, this model is expanding nationwide. By allowing students to gain trade experience and income during training, apprenticeships are gradually reshaping society’s perception of construction as a rewarding career.
Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives
Expanding the talent pool by embracing diversity and inclusion initiatives is another cornerstone strategy reshaping the labor market. On the high-profile Signia by Hilton hotel project in Indianapolis, hiring targets have been set for women (8%), racial minorities (15%), and local Marion County residents (30%)—benchmarks that the project’s managers view not only as social goals but as business imperatives. By partnering with minority-, women-, veteran-, and disabled-owned businesses, this initiative opens pathways for historically underrepresented groups while meeting urgent workforce needs. Outreach programs and pipeline partnerships are making the industry more accessible to groups who have previously been shut out, providing mentorship, scholarships, and support networks that foster long-term success. Diverse teams also foster fresh perspectives, drive innovation, and contribute to the strengthening of local economies.
Technological Integration
Technology continues to revolutionize project planning and execution by providing scalable solutions to labor shortages. Cloud-based hierarchical imitation learning allows robots to learn from skilled workers and assist on site, automating repetitive or physically demanding tasks, enhancing safety, and enabling teams to concentrate on more valuable work. Automation also helps mitigate workforce shortages by ensuring critical steps, such as equipment operation or quality inspections, are performed efficiently. Moreover, augmented reality, drone mapping, and advanced management platforms streamline operations and appeal to tech-savvy workers eager to innovate. Employers benefit from increased transparency, real-time tracking, and improved resource management, helping to compensate for labor shortages. As technological advances continue to progress, the construction industry is attracting younger generations familiar with digital tools, who are seeking careers that combine physical and virtual problem-solving.
Educational Partnerships
Strong partnerships between industry leaders and educational institutions are key to maintaining a skilled labor force. The HITT Futures program, celebrating 20 years in 2025, exemplifies how collaborations serve as a force multiplier. It combines externships, internships, and apprenticeships to introduce students to real-world construction skills and career paths. Strong ties with technical schools and community colleges provide a steady talent pool, with curriculum aligned to industry needs. Educational partners frequently update coursework to reflect industry trends, safety standards, and emerging technologies. These partnerships expose students to current practices and site culture early, demystifying construction work and creating a direct path from classroom to job. They also help retain professionals by fostering a sense of community long before the hiring process begins.
Government Investments
Public investment plays a vital role in workforce development. The UK has committed £600 million to enhance construction skills, funding various courses, apprenticeships, and worker upskilling, to build 1.5 million homes by 2029. This illustrates the influence of policy and funding on the industry. In the US, federal and state efforts direct resources toward vocational training and on-the-job programs, often through public-private partnerships or tax incentives. These initiatives help address labor shortages while bolstering economic resilience and community well-being. Government investments—such as grants, school funding, and equipment—are essential in maintaining construction’s role as a key driver of economic opportunity for all.
Conclusion
The construction labor shortage presents a defining challenge for the industry’s future, but it is also spurring transformative solutions. Through robust apprenticeship programs, targeted diversity efforts, strategic application of technology, deep educational partnerships, and government investment, the industry is building new pathways to career success. These approaches create not only a more inclusive and sustainable workforce but also ensure the sector remains prepared for whatever demands the future may bring. By working collaboratively and adopting a forward-looking mindset, stakeholders can help guarantee that the construction industry not only recovers from the current shortage but also emerges stronger and more adaptable than ever before.